Akira Sakakibara, PhD
Research
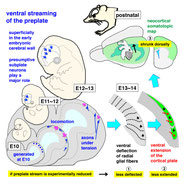
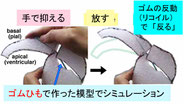
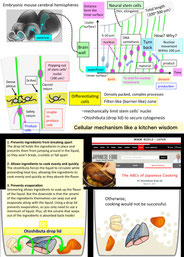
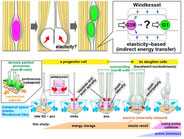
We focus on cell biological aspects of neuronal morphogenesis in the developing brain. Neuronal migration and polarization require cytoskeletal organization and remodeling, however, the cytoskeletal dynamics in migrating neurons in vivo is not well understood. To clarify how cytoskeletons are involved in neuronal migration and polarization, we live-monitor the cytoskeletal dynamics in situ. By using this approach, we have found interesting behaviors of centrosome during two distinct modes of polarization in neocortical neurons in slice culture. In multipolar neurons axons form by tangential extension of a dominant process and the centrosome orients toward the growing axon, while in locomoting neurons an axon forms opposite to the direction of migration and the centrosome localizes to the base of the leading process. These findings suggest that MT organization between processes may alter centrosomal localization and that centrosomal positioning does not direct process formation in neocortical neurons. To further dissect molecular mechanisms underlying the centrosomal movements, loss of function experiments of MT-related proteins are ongoing.
History
1997 PhD in Cell Biology, The Graduate University for Advanced Studies, National Institute for Physiological Sciences, Okazaki, Japan (Shoichiro Tsukita lab.)
1997 Postdoctoral Fellow, National Institute of Neuroscience, National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry, Kodaira Japan (Seisuke Hattori & Shun Nakamura lab.)
2001 Postdoctoral Fellow, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, USA (Rick Horwitz lab.)
2006 Postdoctoral Fellow, Cancer Research UK London Research Institute, London, UK (Ralf Adams lab.)
2008 Assistant Professor, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, Nagoya, Japan (Takaki Miyata lab.)
Publications
Sakakibara, A., Sato, T., Ando, R., Noguchi, N., Masaoka, M., Miyata, T.
Cereb. Cortex in press
Namba, T., Kibe, Y., Funahashi, Y., Nakamuta, S., Takano, T., Ueno, T., Shimada, A., Kozawa, S., Okamoto, M., Shimoda, Y., Oda, K., Wada, Y., Masuda, T., Sakakibara, A., Igarashi, M., Miyata, T., Faivre-Sarrailh, C., Takeuchi, K., Kaibuchi, K. (2014)
Pioneering axons regulate neuronal polarization in the devveloping cerebral cortex.
Neuron 81: 814-829
Okamoto, M., Namba, T., Shinoda, T., Kondo, T., Watanabe, T., Inoue, Y., Takeuchi, K., Enomoto, Y., Ota, K., Oda, K., Wada, Y., Sagou, K., Saito, K., Sakakibara, A., Kawaguchi, A., Nakajima, K., Adachi, T., Fujimori, T., Ueda, M. Hayashi, S., Kaibuchi, K., Miyata, T. (2013)
TAG-1–assisted progenitor elongation streamlines nuclear migration to optimize subapical crowding.
Nat. Neurosci. 16: 1556-1566
Sakakibara, A., Ando, R., Sapir, T., Tanaka, T. (2013)
Microtubule dynamics in neuronal morphogenesis.
Open Biol. 3:130061
Sapir, T., Levy, T., Sakakibara, A., Rabinkov, A., Miyata, T., Reiner, O. (2013)
Shootin1 acts in concert with KIF20B to promote polarization of migrating neurons.
J. Neurosci. 33:11932-11948
Xie, M.-J., Yagi, H., Kuroda, K., Wang, C.-C., Komada, M., Zhao, H., Sakakibara, A., Miyata, T. Nagata, K., Iguchi, T., Sato, M. (2013)
WAVE2-Abi2 complex controls growth cone activity and regulates the multipolar-bipolar transition as well as the initiation of glia-guided migration.
Cereb. Cortex 23:1410-1423
Pérez-Martínez, F.J., Luque-Río, Á., Sakakibara, A., Hattori, M., Miyata, T., Luque, J.M. (2012)
Reelin-dependent ApoER2 downregulation uncouples newborn neurons from progenitor cells.
Biol. Open 1:1258-1263
Nakamuta, S., Funahashi, Y., Namba, T., Arimura, N., Picciotto, M.R., Tokumitsu, H., Soderling, T.R., Sakakibara, A., Miyata, T., Kamiguchi, H., Kaibuchi, K. (2011)
Local application of neurotrophins specifies axons through inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, calcium, and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases.
Sci. Signal. 4:ra76
Miyata, T., Ono, Y., Okamoto, M., Masaoka, M., Sakakibara, A., Kawaguchi, A., Hashimoto, M., Ogawa, M. (2010)
Migration, early axonogenesis, and Reelin-dependent layer-forming behavior of early/posterior born Purkinje cells in the developing mouse lateral cerebellum.
Neural Dev. 5:23
Wang, Y., Nakayama, M., Pitulescu, M.E., Schmidt, T.S., Bochenek, M.L., Sakakibara, A., Adams, S., Davy, A., Deutsch, U., Barberis, A., Benjamin, L. E., Makinen, T., Nobes, C. D., Adams, R. H. (2010)
Ephrin-B2 controls VEGF-induced angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis.
Nature 465:483-486
Minobe, S., Sakakibara, A., Ohdachi, T., Kanda, R., Kimura, M., Nakatani, S., Tadokoro, R., Ochiai, W., Nishizawa, Y., Mizoguchi, A., Kawauchi, T., Miyata, T. (2009)
Rac is involved in the interkinetic nuclear migration of cortical progenitor cells.
Neurosci. Res. 63:294-301
Ochiai, W., Nakatani, S., Takahara, T., Kainuma, M., Masaoka, M., Minobe, S., Namihira, M., Nakashima, K., Sakakibara, A., Ogawa, M., Miyata, T. (2009)
Periventricular notch activation and asymmetric Ngn2 and Tbr2 expression in pair-generated neocortical daughter cells.
Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 40:225-233
Sakakibara, A., Horwitz, A.F. (2006)
Mechanism of polarized protrusion formation on neuronal precursors migrating in the developing chicken cerebellum.
J. Cell Sci. 119:3583-3592
Sakakibara, A., Hattori, S., Nakamura, S., Katagiri, T. (2003)
A novel hematopoietic adaptor protein, Chat-H, positively regulates T cell receptor-mediated interleukin-2 production in Jurkat cells.
J. Biol. Chem. 278:6012-6017
Sakakibara, A., Ohba, Y., Kurokawa, K., Matsuda, M., Hattori, S. (2002)
Novel function of Chat in controlling cell adhesion via Cas-Crk-C3G-pathway-mediated Rap1 activation.
J. Cell Sci. 115:4915-4924
Sakakibara, A., Hattori, S. (2000)
Chat, a Cas/HEF1-associated adaptor protein that integrates multiple signaling pathways.
J. Biol. Chem. 275:6404-6410
Moroi, S., Saitou, M., Fujimoto, K., Sakakibara, A., Furuse, M., Yoshida, O., Tsukita, S. (1998)
Occludin is concentrated at tight junctions of mouse/rat but human/guinea pig Sertoli cells in testes.
Am. J. Physiol. 274:C1708-C1717
Hashimoto, H., Sakakibara, A., Yamasaki, M. and Yoda, K. (1997)
Saccharomyces cerevisiae VIG9 encodes GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase, which is essential for protein glycosylation.
J. Biol. Chem. 272:16308-16314
Sakakibara, A., Furuse, M., Saitou, M., Ando-Akatsuka, Y., Tsukita, S. (1997)
Possible involvement of phosphorylation of occludin in tight junction formation.
J. Cell Biol. 137:1397-1401
Ando-Akatsuka, Y., Saitou, M., Hirase, T., Kishi, M., Sakakibara, A., Itoh, M., Yonemura, S., Furuse, M., Tsukita, S. (1996)
Interspecies diversity of occludin sequence: cDNA cloning of human, mouse, dog, and rat-kangaroo homologues.
J. Cell Biol. 133:43-47